| Admiralty law |
|---|
| History |
| Features |
|
| Contracts of affreightment |
| Types of charter-party |
| Parties |
| Judiciary |
| International conventions |
| International organisations |
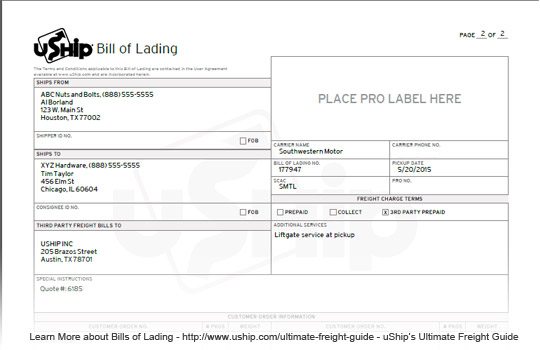
A waybill (UIC) is a document issued by a carrier giving details and instructions relating to the shipment of a consignment of goods. Typically it will show the names of the consignor and consignee, the point of origin of the consignment, its destination, and route. Most freight forwarders and trucking companies use an in-house waybill called a house bill. These typically contain 'conditions of contract of carriage' terms on the back of the form that cover limits to liability and other terms and conditions.[1]
A waybill is similar to that of a courier's receipt, which contains the details of the consignor and the consignee and the point of origin and the destination.[2]
- Bulk E-Way Bill Generation Tool (Ver 1.0.0918) Welcome to the Bulk E-Way Bill generation tool. Using this tool, one can prepare the JSON file to generate the large number of e-Way Bills in one go. This tool enables the tax payers to prepare the bulk requests in two ways.
- E-Invoice Trial web-site is released in Bulk upload facility can be used here for IRN generation. E-Invoicing System for sandbox API interface (for testing) has been released on portal https://einv-apisandbox.nic.in.
- Login for generation of Waybill Key Nos. You have to enter the same User-id and Password, which is being used for eFiling of Return. If you commit any mistake in doing so, you may re-enter those. You have to click the link ‘Generate bulk-Waybill keys’. You will get the form for generate bulk Waybill.
Air waybills[edit]
Preparing Bulk EWB request file There are two methods for generating the Bulk EWB requests. First, the tax payers can prepare the Bulk EWB request file as follows. In the bulk EWB generation method, the request for e-way bill is accepted in the JSON format. Htc one m8 marshmallow download. Please refer to excel file for the format and parameters of the JSON request file.
Most airlines use a different form called an air waybill which lists additional items such as airport of destination, flight number, and time.[3]
Sea waybills[edit]
The UK Carriage of Goods by Sea Act 1992 s.1(1) applies to:
- bills of lading s.1(2),
- sea waybills s.1(3), and
- ships' delivery orders s.1(4),
. whether in paper or electronic form s.1(5). Session key generation in ssl.
Under s.1(3) of the Act, a sea waybill is: 'any document which is not a bill of lading but is such a receipt for goods as contains a contract for the carriage of goods by sea; and identifies the person to whom delivery of the goods is to be made by the carrier in accordance with that contract'.
s.2 continues: '.a person who becomes the person who (without being an original party to the contract of carriage) is the person to whom delivery of the goods to which a sea waybill relates is to be made by the carrier in accordance with that contract . shall (by virtue of becoming the person to whom delivery is to be made) have transferred to and vested in him all rights of suit under the contract of carriage as if he had been a party to the contract of carriage'.
Note: the UK's Contracts (Rights of Third Parties) Act 1999 does NOT apply to contracts for the carriage of goods by sea.
Bulk Generation Of Waybill Keys Code
References[edit]
- ^'What is a waybill? definition and meaning'. WebFinance, Inc. Retrieved 7 October 2013.
- ^'What are Courier's Receipt'. JCtrans Technology Co., Ltd. Retrieved 7 October 2013.
- ^'What is air waybill (AWB)? definition and meaning'. WebFinance, Inc. Retrieved 7 October 2013.
See also[edit]
- ^GST MUNIMJI (2018-06-03), FIVE FACST ON GST (GOODS & SERVICES TAX) E-WAYBILL, retrieved 2018-06-03